Query best practices — Sensedia Analytics API
To ensure fast and stable performance for all users, we strongly recommend following these best practices when querying the Sensedia Analytics API.
These recommendations are especially important in high-volume and multi-tenant environments, as they directly contribute to cluster stability, lower latency, and a better overall platform experience.
1. Always filter by time (date range)
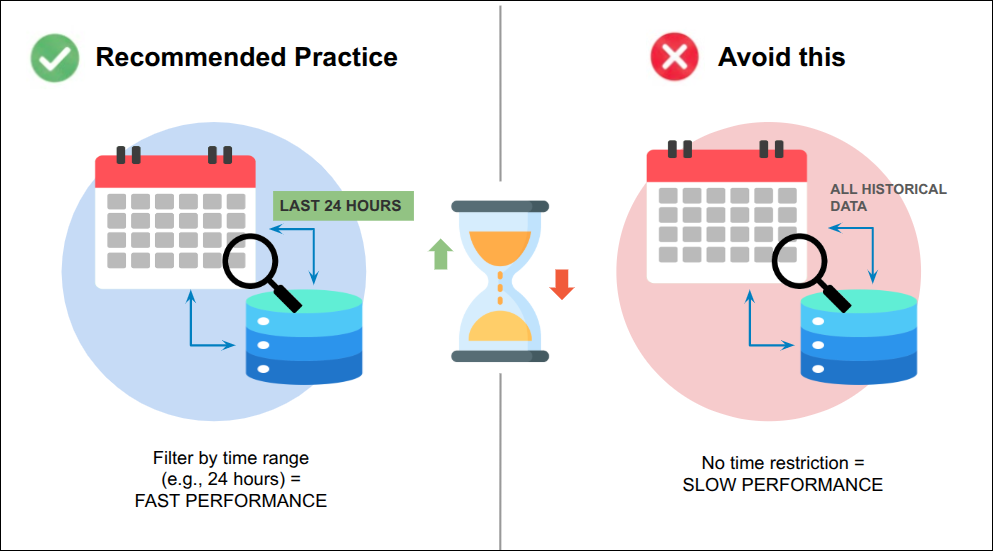
Search on temporal data is optimized when indexes follow the time-series pattern.
-
Recommended practice: Always include a time range filter in your queries.
-
Avoid: Queries that attempt to retrieve data from the entire historical dataset without time restrictions.
-
Optimization: Limit the query to the smallest time window necessary. For example, querying 24 hours of data is significantly faster than querying 30 days.
2. Limit response size (pagination)

Restricting the number of documents returned in a single request is critical for both network performance and query efficiency.
-
Use pagination: Use parameters such as
sizeandfrom(orpageandlimit) to control the number of results returned and the query offset. -
Smart limits: Keep the
size(document limit per request) at a reasonable value, for example, a maximum of 1,000 or 10,000 records, according to your environment’s capacity.
3. Select only the required fields
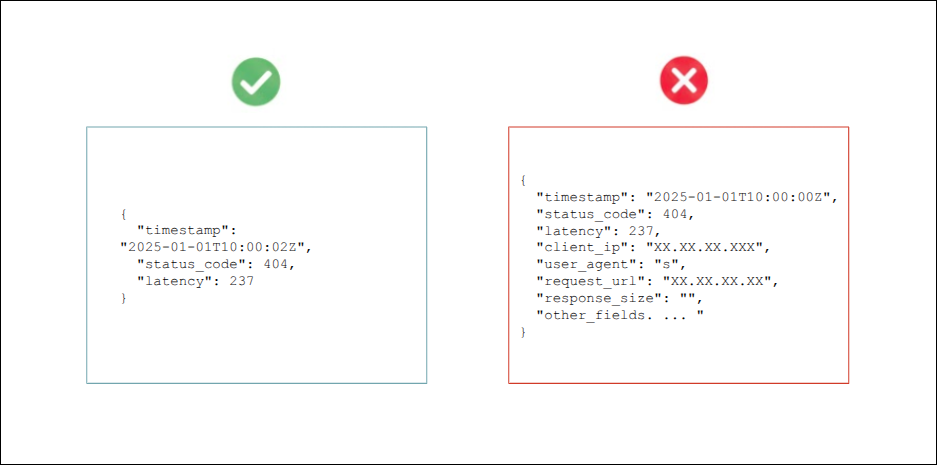
By default, OpenSearch returns the full JSON document (_source).
If your application requires only a subset of fields, explicitly specify which fields are needed.
-
Use
_source_includesor field parameters: Request only the fields that will be used, for example:fields=timestamp,status_code,latency.Benefit: This significantly reduces bandwidth consumption and processing time in the OpenSearch cluster.
4. Optimize aggregations
Aggregations are used to compute metrics such as counts, averages, and sums, and they often represent the most expensive part of a query.
-
Filter before aggregating: Always apply strict filters — especially the time filter — before executing aggregations. The fewer documents processed, the faster the response.
-
Avoid high-cardinality aggregations: Avoid grouping by fields with an extremely high number of unique values, such as transaction IDs. Prefer fields with controlled cardinality, such as
status_codeorapi_name. -
Bucket limitation: Do not request an excessive number of buckets in a single aggregation. If you need more than 100 buckets, consider performing multiple queries or using sampling techniques.
5. Prefer terms over wildcards
How you structure your search queries directly impacts performance.
-
Correct query type selection: Use
termexclusively for exact matches onkeywordfields andmatchfor full-text searches on analyzed text fields, avoiding unnecessary text processing. Avoidwildcard(*) and regular expression queries whenever possible, as they require extensive index scanning and consume significantly more CPU and I/O. -
If you must use
wildcard: Avoid starting the expression with "*". For example, preferapi_name*instead of*api_name.
6. Avoid unnecessary sorting
Sorting results is an expensive operation and should be avoided whenever possible.
-
Recommended practice: If the default sort by timestamp in descending order is sufficient, avoid specifying additional sort fields.
-
When sorting is required: Prefer numerical or date fields that are not analyzed (
keywordtype fields).
Avoid sorting by unstructured text fields.
By following these guidelines, your clients will maximize query performance and help maintain the optimal operation of the Sensedia Analytics environment.
Share your suggestions with us!
Click here and then [+ Submit idea]