JWT Validation
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained method for transferring transmission between two parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted since the token is digitally signed.
JWTs can be signed by using a secret (with the HMAC algorithm) or a pair of public/private keys using RSA.
To read more about it, access this website: https://jwt.io/.
Generating a token
| Before we make the call to generate the JWT token, we need to make a call to generate the Authorization Code. To know how to generate it, click here. |
To use this interceptor, an app must have been created, so that we can access the client ID and client secret.
To generate the JWT, it is necessary to make a POST request to the endpoint <gateway url>/oauth/access-token.
The header should contain the following information:
Authorization : Basic client_id:client_secret
The client_id:client_secret must be a string converted to Base64, using the app data.
|
Here is an example of a header with the client ID and secret converted to Base64:
Authorization : Basic ZjkyMTIxNzMtZTcwNS0zNzNiLWE2OTgtNjE5MjNlMzc4MzU5OjAyYWI1Mjg4LTkyZGItM2FiMy05OWZkLWZhYzRhZjg1N2Q4MQ==
In the body, we must inform the "code" generated by the grant-code endpoint, with a few more items in the format x-www-form-urlencoded:
"grant_type": "urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer" "code" : "8748d39f-1d4f-311f-92c6-4b279db1b317"
|
In addition to generating a JWT, you can also create an encrypted token using the JWE (JSON Web Encryption) standard. To learn how to generate a JWE and protect the token content with encryption, see JWE (JSON Web Encryption). |
Lastly, your access token will be generated again and should appear as the example below:
{
"access_token": "ca81cb16-43e4-3e96-aaea-4861e7791dc7",
"refresh_token": "677b881a-d0b6-3b29-b9a8-f0cdb50ce035",
"token_type": "access_token",
"expires_in": 3600
}
If your API returns the status code 401 Unauthorized when using this interceptor, the token may be invalid. See more details on this page of our FAQs.
|
Flow
This interceptor can only be inserted in the request flow and two pieces of information need to be configured: Location and Name.
Location options are:
-
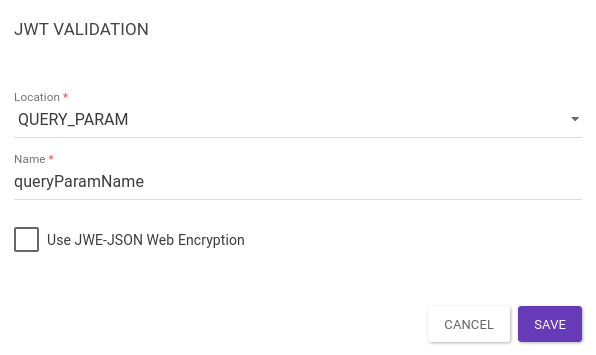
Query Param: validates the existence of a JWT informed via query param.
-
The property "Name" defines the expected query param name.
-
-
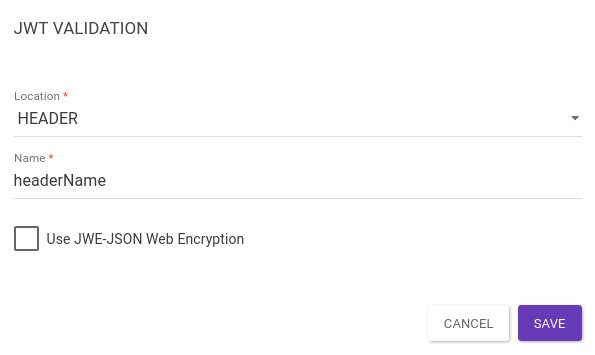
Header: validates an existing JWT in the header.
-
The property "Name" defines the expected header name.
-
-
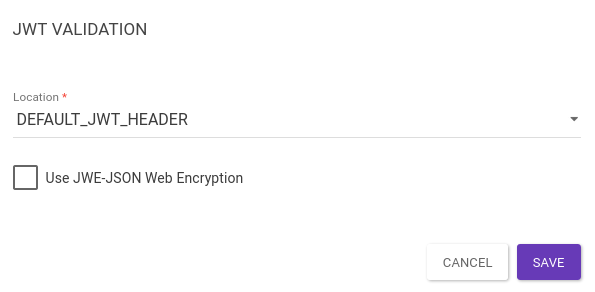
Default JWT Header: validates an existing JWT in the header.
-
In this case, there is no property "name"; the JWT is expected in the header
Authorization.
-
JWE (JSON Web Encryption)
As we mentioned in the beginning of this page, JWT is a pattern that allows transmitting tokens from one party to another with security regarding the legitimacy of the token sent. It is usual for this pattern to be used to send additional information via "claims".
However, it’s important to remember that JWT is a pattern that ensures data reliability, not confidentiality. Sensitive information transmitted in the body of the token can be intercepted and exposed.
The JWE (JSON Web Encryption) adds an extra layer of security to the token by encrypting the transmitted data. This allows you to extend the functionality of JWT so that, in addition to ensuring authenticity and integrity, it also guarantees the confidentiality of the transmitted information.
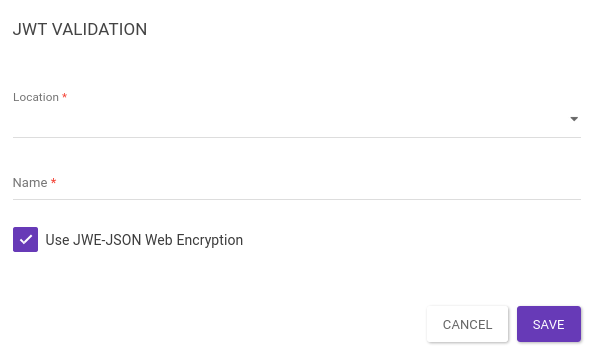
Option Use JWE – JSON Web Encryption
When the Use JWE – JSON Web Encryption option is enabled, the encrypted token in the request is validated, decrypted, and then forwarded to the backend. This process ensures that only authorized systems can access the token’s content, reinforcing end-to-end security in the communication between the parties.
Requirements to Run the Flow
To correctly execute the flow, you must have:
-
An API with OAuth interceptors configured for JWT and JWT Validation interceptor, with the JWE – JSON Web Encryption feature enabled.
-
An App associated with the API.
-
A Plan linked to the API.
| Make sure that the OAuth 2.0 API is available in your environment. If not, you’ll need to create it before proceeding. |
The next steps depend on the requirements above. Ensure that all prerequisites are completed before continuing.
Generating the JWE
The JWE generation process involves two main steps:
1. Generate grant code
Generating a grant code is an essential step to create the JWE.
Send a POST request to the /oauth/grant-code endpoint of the OAuth API, as shown in the example below:
curl --location '<gateway_url>/oauth/grant-code' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data '{
"client_id": "<app_client_id>",
"extraInfo": {},
"redirect_uri": "http://localhost/",
"state": "string"
}'
Replace:
-
<app_client_id>with the value of your application’s client_id. -
<redirect_url>with the desired redirect URL. -
<gateway_url>with the gateway address for your environment.
{
"redirect_uri": "http://localhost/?state=string&code=**40a7848a-2615-49ba-ae27-cff175095c16**"
}
After sending the request, a response containing the "redirect_uri" will be returned.
Copy the "code" value, as it will be required in the next step.
|
The API must include an OAuth interceptor with the JWT option enabled. Otherwise, a bad request error will occur, indicating that the grant type is invalid. Example response
|
2. Generate JWE
With the obtained code, it’s time to generate the JWE. See the example request below.
curl --location 'https://<gateway_url>/oauth/access-token' \
--header 'Authorization: Basic NmM5MWUwNDQtYTJkMS00ZmFiLTkwYjgtMWRhNmMwZDc2YWMzOjI5Y2I4ODE1LWM2ODEtNGIwZC04Yzc2LTg2NzdmMzFlODY2Yg==' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data-urlencode 'grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer' \
--data-urlencode 'code=40a7848a-2615-49ba-ae27-cff175095c16' \
--data-urlencode 'encrypt=true'|
The |
|
In the example above:
|
Adjust the example as needed:
-
Include the
Authorizationheader with your App’s Base64 code. -
Insert the code obtained earlier.
-
Add the
encrypt=trueparameter. -
Replace
<gateway_url>with your environment’s gateway URL.
|
The request must be sent in x-www-form-urlencoded format. |
{
"access_token": "eyJleHAiOjE3NTUyODAxMzIyNDEsImFsZyI6ImRpciIsImVuYyI6IkExMjhHQ00ifQ..6r0yEMyxMrCutmGq.ywwIieYyG79S5G1ZEk1V9HDrYyvNknP_G1u4Wpzw3yW3-FAJT-oHuQUIRGVpqXtphOyEKaw-WNUhZYsasnX6o_Ju8uRLjEPVdeVa8y4SXU1c8wBWXe1jD9GK-TogVPAaaHrHq4q-iUL-gZJiOzsoCm0li3LgwjZPUq8A7RIcWUDSfsSZobow5Hi8xpn16L6V4iCcUZ-UA6hywS_UeR2J7uUPzj8273w8kAXvyWkWqrFnDf7Dv6T7vAY69vI3ZfBUgUquDD38V7gsmGuG6vSdcSRqKCYTvVgGCxbwPARJFxLw3rXE76R1F6GVmzmrSJQCtrcajNH5X_ZJnI9c12mnBGWwKtj8UjsJlsVBn4EAzWtxX6Fl-kXubclS1RW_VtcKXBd_yzBRCKUksR8QoHET2wDKSPJl9hg0-6g9xhvrSo-aVVo4FZkBQoBmAv7FN3C0CNwWJ5nId2mTnwckdAmHWqLpqq3rwcED42pLvy3pnYz4LHU5FZHQrk1Z0kExaVY_YOYJvN6fV-Whc5fSyG82B0R2AQ36AzxQq1-Fcqy9Xw.Ah69e5r8RS1MBqaJgS61wQ",
"token_type": "access_token",
"expires_in": null
}Copy the value of the access_token field. This is your JWE.
|
The use of JWE follows the same pattern as JWT. For more details, see the topic JWT (JSON Web Token). |
Validating the JWE Flow (optional)
To confirm that the token was indeed encrypted, you can use JWT Debugger.
You’ll notice that the token’s content is unreadable, confirming that encryption was applied.
To validate the Use JWE – JSON Web Encryption option:
-
Send a request to your API, including the App’s
client_idand the generatedaccess_token(JWE). -
In the API’s destination field, use a mock that allows you to visualize the decrypted access_token — for example, Supermock Sensedia.
curl --location 'https://api-sensediaqa1.sensedia-eng.com/jwt' \
--header 'client_id: 6c91e044-a2d1-4fab-90b8-1da6c0d76ac3' \
--header 'access_token: eyJleHAiOjE3NTUyODAxMzIyNDEsImFsZyI6ImRpciIsImVuYyI6IkExMjhHQ00ifQ..6r0yEMyxMrCutmGq.ywwIieYyG79S5G1ZEk1V9HDrYyvNknP_G1u4Wpzw3yW3-FAJT-oHuQUIRGVpqXtphOyEKaw-WNUhZYsasnX6o_Ju8uRLjEPVdeVa8y4SXU1c8wBWXe1jD9GK-TogVPAaaHrHq4q-iUL-gZJiOzsoCm0li3LgwjZPUq8A7RIcWUDSfsSZobow5Hi8xpn16L6V4iCcUZ-UA6hywS_UeR2J7uUPzj8273w8kAXvyWkWqrFnDf7Dv6T7vAY69vI3ZfBUgUquDD38V7gsmGuG6vSdcSRqKCYTvVgGCxbwPARJFxLw3rXE76R1F6GVmzmrSJQCtrcajNH5X_ZJnI9c12mnBGWwKtj8UjsJlsVBn4EAzWtxX6Fl-kXubclS1RW_VtcKXBd_yzBRCKUksR8QoHET2wDKSPJl9hg0-6g9xhvrSo-aVVo4FZkBQoBmAv7FN3C0CNwWJ5nId2mTnwckdAmHWqLpqq3rwcED42pLvy3pnYz4LHU5FZHQrk1Z0kExaVY_YOYJvN6fV-Whc5fSyG82B0R2AQ36AzxQq1-Fcqy9Xw.Ah69e5r8RS1MBqaJgS61wQ'After execution, the backend will receive the already decrypted token, allowing you to validate the complete flow of the Use JWE – JSON Web Encryption feature.
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJhdWQiOiJhcGktYXV0aG9yaXphdGlvbi5zaGFyZWQuc3ZjLmNsdXN0ZXIubG9jYWwiLCJpc3MiOiIxMC4xMzUuNTAuODUiLCJqdGkiOiI0N2UxM2Q3Mi05OGQ1LTRhOGQtODgzYi05NzFkMDgxYmQ0OTIiLCJzdWIiOiI2YzkxZTA0NC1hMmQxLTRmYWItOTBiOC0xZGE2YzBkNzZhYzMiLCJleHAiOjAsImlhdCI6MTc1NTI4MDEzMiwiQXBwOiAiOiJBcHAiLCJDb2RlOiAiOiI0MGE3ODQ4YS0yNjE1LTQ5YmEtYWUyNy1jZmYxNzUwOTVjMTYifQ.xJ7YfU_v0mb4ZTMmglPcj5g5zuJbDlFZnRoE-e8AplM",
"token_type": "access_token",
"expires_in": null
}Share your suggestions with us!
Click here and then [+ Submit idea]