Marshal
The Marshal EIP converts the internal format (objects or structures) into an external format (such as JSON or XML) for communication or storage. For example, it can transform a Java object into a JSON or XML representation.
Custom
In the list of available data format types in Data Format Type, there is the Custom option.
With it, you can use Excel as a reference, allowing the integration flow to process files in .xls and .xlsx formats.
This data format will convert the rows of the specified spreadsheet into an array of JSON objects. The JSON object generated for each cell will contain, in addition to the value, metadata about the data type.
| Spreadsheet visual styles (cell color, font color, bold, borders, and others) are not imported. |
To use the component, consider these guidelines:
-
The setHeader
SensediaExcelFormatindicates whether the file is.xlsor.xlsx.-
If the value provided is different, the component will throw an error.
-
If the setHeader is not sent,
.xlsxwill be assumed by default.
-
-
The setHeader
SensediaExcelSheetNamesprovides a list of sheet names, separated by commas.-
Only the sheets listed in the setHeader will be processed.
-
If any listed sheet does not exist in the file, it will be ignored.
-
-
If the setHeader
SensediaExcelSheetNamesexists but none of the names match a sheet in the file, the component will throw an error. -
The use of formulas is allowed. However, if the formula is incorrect, the cell in Excel will indicate an error.
JSON Format
After converting an Excel file to JSON, the data is organized as shown in the JSON Schema below:
{
"type": "object",
"$schema": "https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/schema",
"title": "Excel spreadsheet data schema",
"description": "Schema for a data structure representing one or more spreadsheets with rows and cells.",
"properties": {
"sheets": {
"description": "An array containing data for each sheet",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"description": "The name of the sheet.",
"type": "string"
},
"rows": {
"description": "The rows within a single sheet",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"cells": {
"description": "The rows within a single row",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"v": {
"description": "The value of the cell. Can be a string, a number, or a boolean.",
"oneOf": [
{ "type": "string" },
{ "type": "number" },
{ "type": "boolean" }
]
},
"addr": {
"description": "The address of the cell (e.g., 'A1').",
"type": "string"
},
"type": {
"description": "The data type of the cell.",
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"str",
"num",
"bool",
"blank",
"formula"
],
"default": "str"
},
"fmt": {
"description": "The formatting string for the cell's value.",
"type": "string",
"default": "General"
}
},
"required": [
"addr"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
},
"required": [
"cells"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
},
"required": [
"name",
"rows"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
},
"required": [
"sheets"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}Excel vs. JSON
Now, compare a spreadsheet with its version in JSON format:
Excel
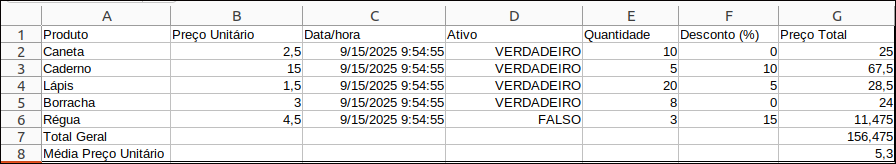
JSON
{
"sheets": [
{
"name": "Sheet1",
"rows": [
{
"cells": [
{
"v": "Produto",
"addr": "A1"
},
{
"v": "Preço Unitário",
"addr": "B1"
},
{
"v": "Data/hora",
"addr": "C1"
},
{
"v": "Ativo",
"addr": "D1"
},
{
"v": "Quantidade",
"addr": "E1"
},
{
"v": "Desconto (%)",
"addr": "F1"
},
{
"v": "Preço Total",
"addr": "G1"
}
]
},
{
"cells": [
{
"v": "Caneta",
"addr": "A2"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 2.5,
"addr": "B2"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 45915.4131373611,
"addr": "C2",
"fmt": "m/d/yyyy\\ h:mm:ss"
},
{
"type": "bool",
"v": true,
"addr": "D2",
"fmt": "\"TRUE\";\"TRUE\";\"FALSE\""
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 10,
"addr": "E2"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 0,
"addr": "F2"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 25,
"addr": "G2"
}
]
},
{
"cells": [
{
"v": "Caderno",
"addr": "A3"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 15,
"addr": "B3"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 45915.4131373611,
"addr": "C3",
"fmt": "m/d/yyyy\\ h:mm:ss"
},
{
"type": "bool",
"v": true,
"addr": "D3",
"fmt": "\"TRUE\";\"TRUE\";\"FALSE\""
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 5,
"addr": "E3"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 10,
"addr": "F3"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 67.5,
"addr": "G3"
}
]
},
{
"cells": [
{
"v": "Lápis",
"addr": "A4"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 1.5,
"addr": "B4"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 45915.4131373611,
"addr": "C4",
"fmt": "m/d/yyyy\\ h:mm:ss"
},
{
"type": "bool",
"v": true,
"addr": "D4",
"fmt": "\"TRUE\";\"TRUE\";\"FALSE\""
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 20,
"addr": "E4"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 5,
"addr": "F4"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 28.5,
"addr": "G4"
}
]
},
{
"cells": [
{
"v": "Borracha",
"addr": "A5"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 3,
"addr": "B5"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 45915.4131373611,
"addr": "C5",
"fmt": "m/d/yyyy\\ h:mm:ss"
},
{
"type": "bool",
"v": true,
"addr": "D5",
"fmt": "\"TRUE\";\"TRUE\";\"FALSE\""
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 8,
"addr": "E5"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 0,
"addr": "F5"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 24,
"addr": "G5"
}
]
},
{
"cells": [
{
"v": "Régua",
"addr": "A6"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 4.5,
"addr": "B6"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 45915.4131373611,
"addr": "C6",
"fmt": "m/d/yyyy\\ h:mm:ss"
},
{
"type": "bool",
"v": false,
"addr": "D6",
"fmt": "\"TRUE\";\"TRUE\";\"FALSE\""
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 3,
"addr": "E6"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 15,
"addr": "F6"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 11.475,
"addr": "G6"
}
]
},
{
"cells": [
{
"v": "Total Geral",
"addr": "A7"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 156.475,
"addr": "G7"
}
]
},
{
"cells": [
{
"v": "Média Preço Unitário",
"addr": "A8"
},
{
"type": "num",
"v": 5.3,
"addr": "G8"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}Code example
This flow exposes a REST endpoint (GET /teste-excel) that, when called, downloads an Excel file from an SFTP server, converts its content to JSON, and returns the result.
The processing occurs as follows:
-
Receives the REST request.
-
Logs the start of the file download via SFTP.
-
Downloads the file from the SFTP server.
-
Logs the completion of the download and the conversion to JSON.
-
Converts the content to
byte[]. -
Defines in the setHeader the sheets to be processed (
test1,test2). -
Uses
marshalwith theexcel(custom) data format to transform the file into JSON. -
Defines the
Content-TypesetHeader toapplication/jsonfor the response.
- from:
uri: rest:get:/teste-excel
steps:
- log:
message: "Iniciando o download do arquivo via SFTP."
- pollEnrich:
expression:
simple: "sftp:eu-central-1.sftpcloud.io:22/download?username={{user}}&password={{pass}}&passiveMode=true&delete=false&fileName={{file}}&binary=true&knownHostsFile=/dev/null&strictHostKeyChecking=no"
- log:
message: "Download concluído. Convertendo para JSON."
- convertBodyTo:
type: byte[]
- setHeader:
name: SensediaExcelSheetNames
expression:
constant:
expression: test1,test2
- marshal:
custom:
ref: excel
- setHeader:
name: Content-Type
constant: application/json|
Excel can also be used in flows with the EIP unmarshal(to transform JSON files into Excel).
|
Examples
See examples of other formats:
-
CSV
-
The message will be converted to
csv. -
No additional parameters are required.
-
- marshal:
csv: {}-
JSON
-
The message will be converted to
json. -
The
Jacksonlibrary will be used to serialize the message body.
-
- marshal:
json:
library: Jackson-
XML
-
The message will be converted to XML.
-
The
jacksonXmlformat uses the Jackson library, but there is also a genericxmlformat.
-
- marshal:
jacksonXml: {}
- marshal:
xml: {}See how to add a data format directly through the EIP form on the Diagram tab:
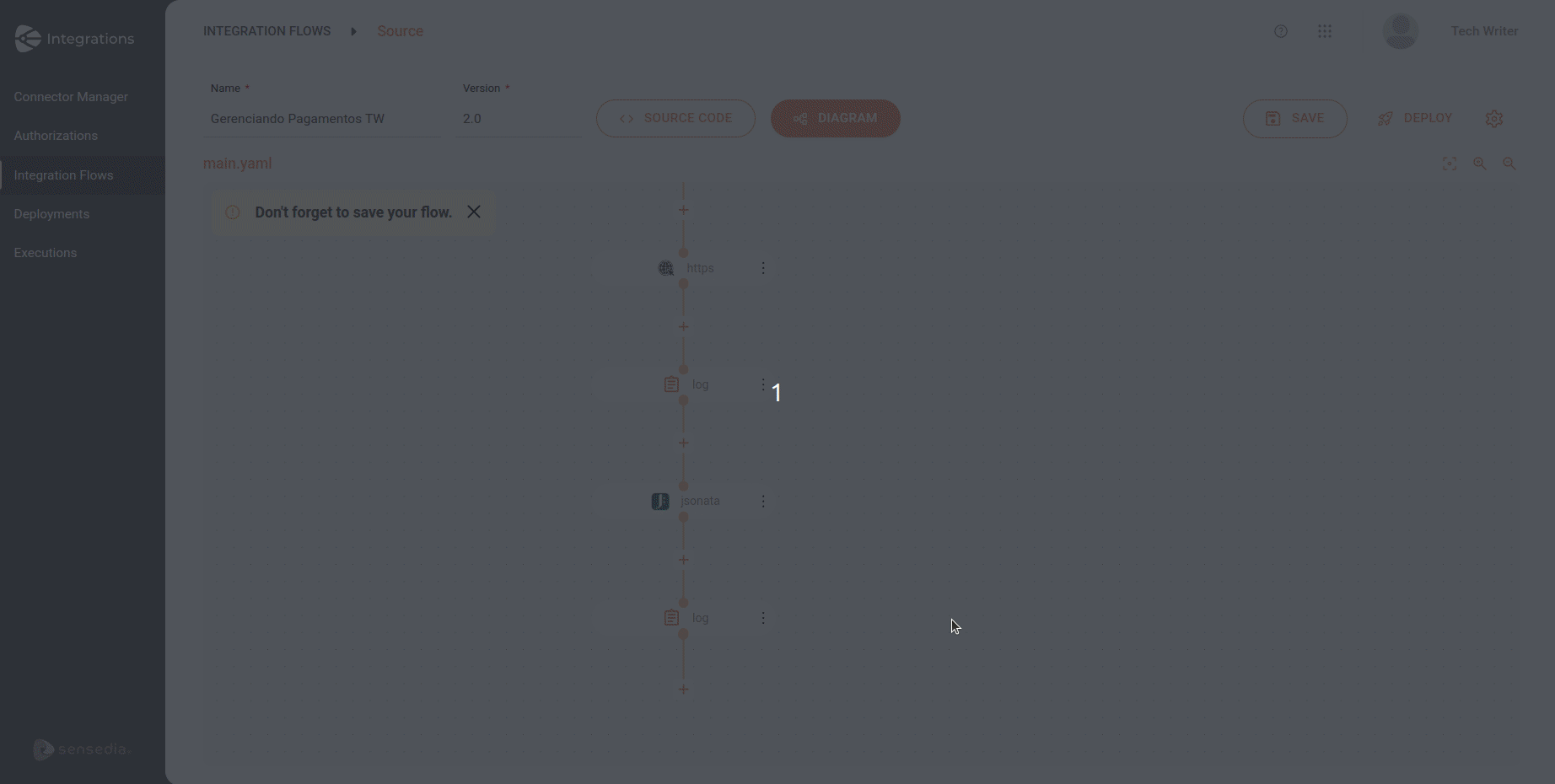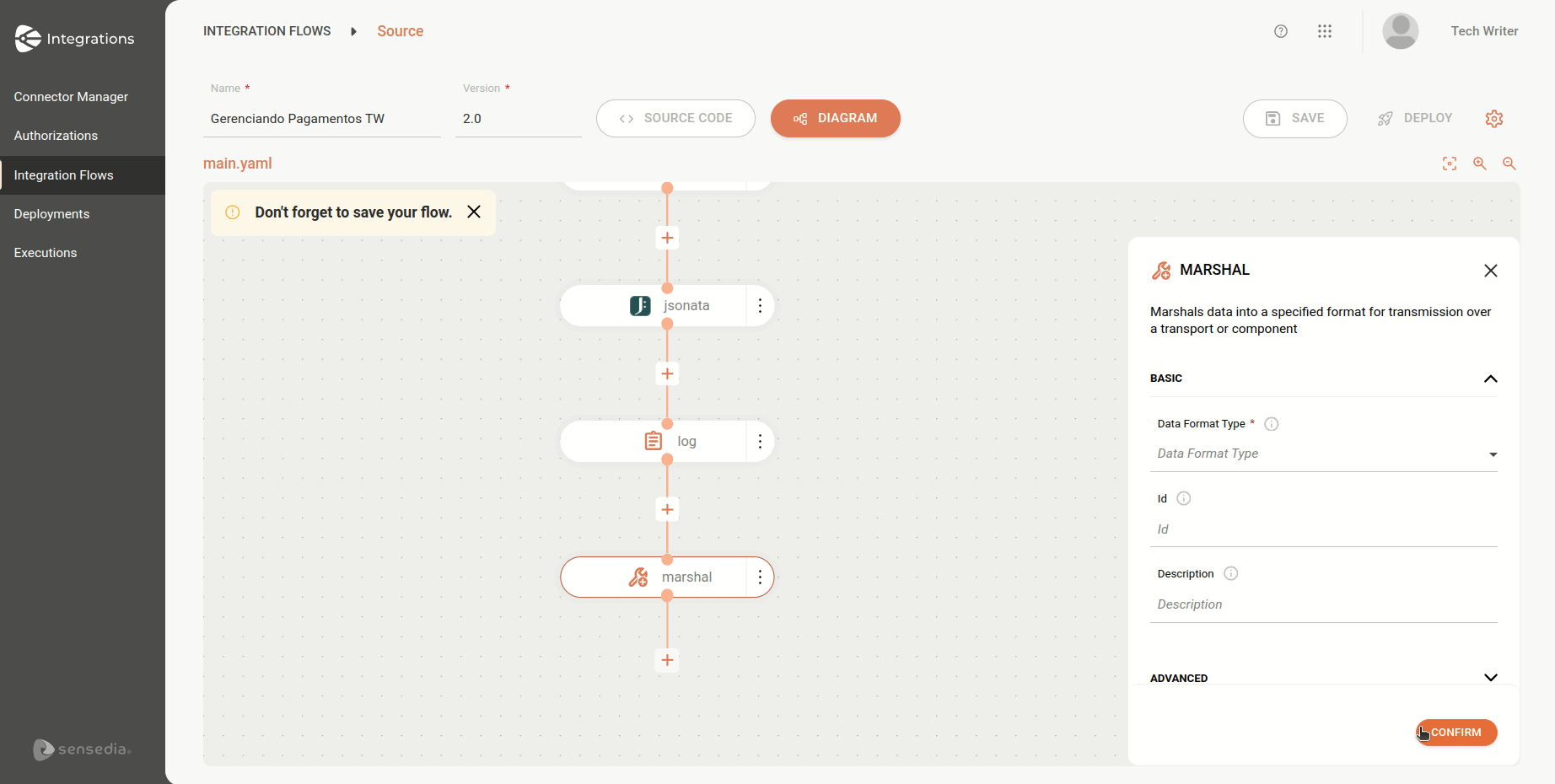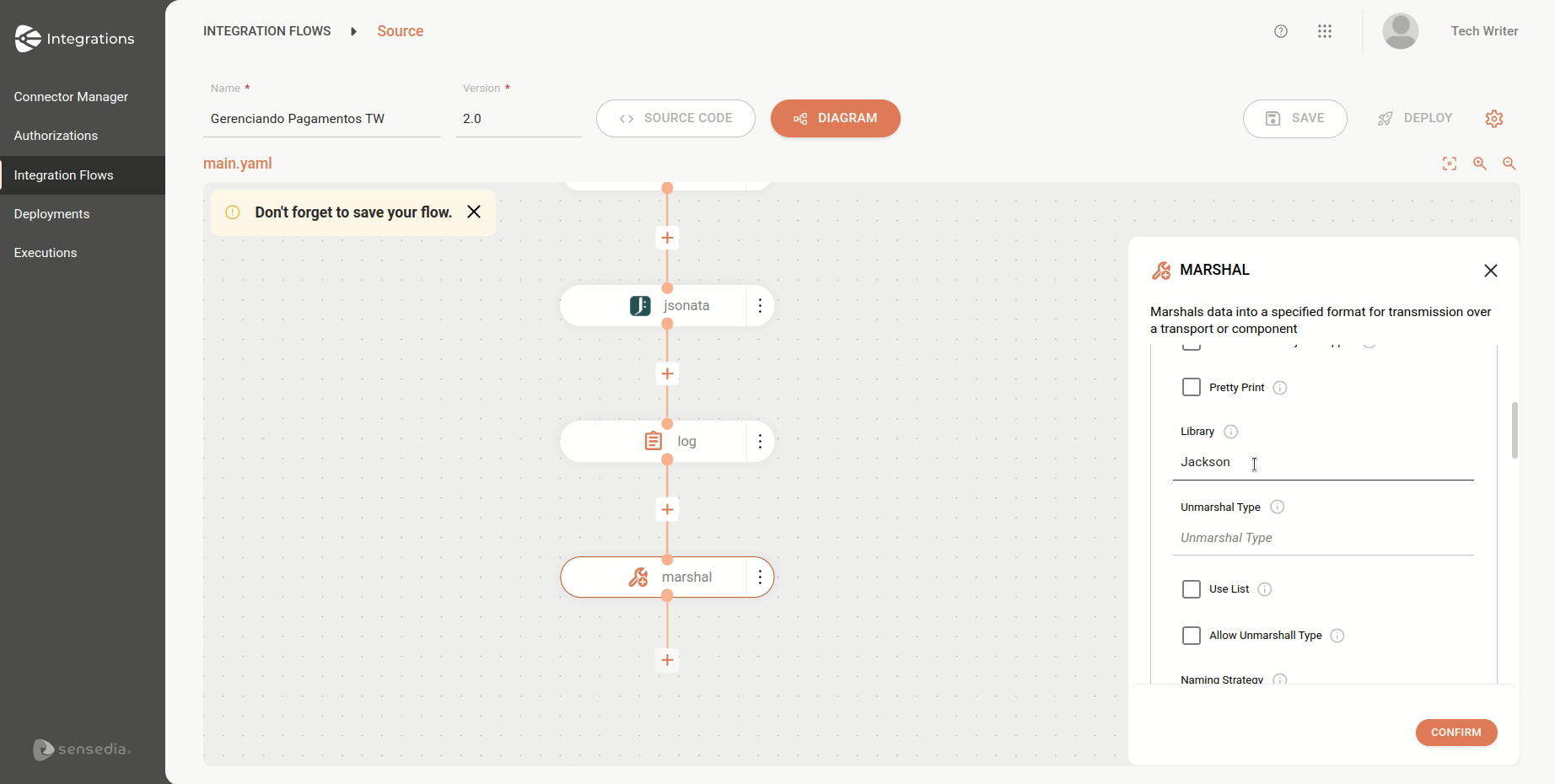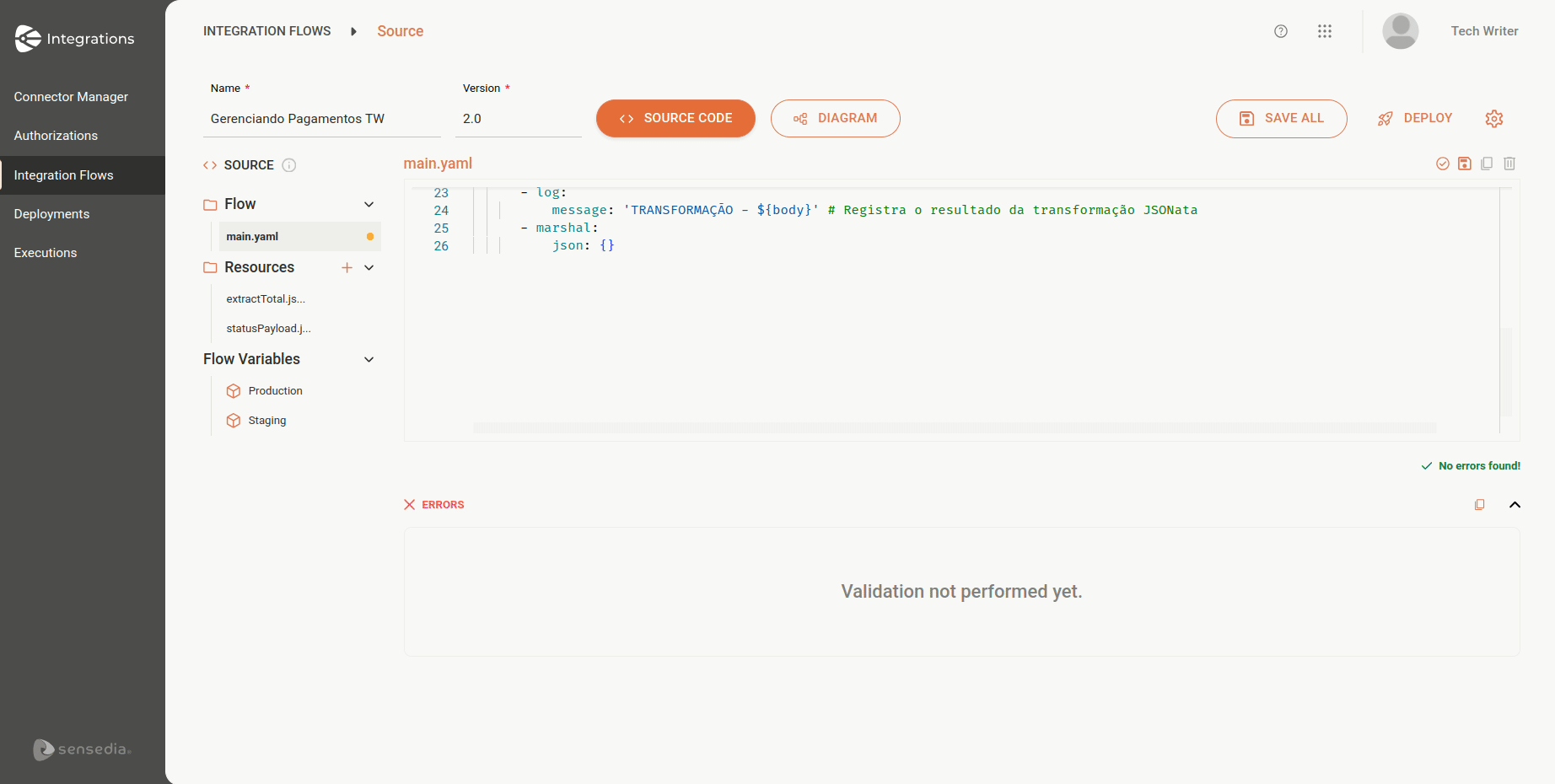
| When selecting the JSON format, the Library field is automatically filled with the default value "Jackson". Since it is the default, it is not displayed in the flow script in the Source tab, appearing only if changed to a different value. |
Share your suggestions with us!
Click here and then [+ Submit idea]