HTTPS and JSONata: Payment Management
Use case
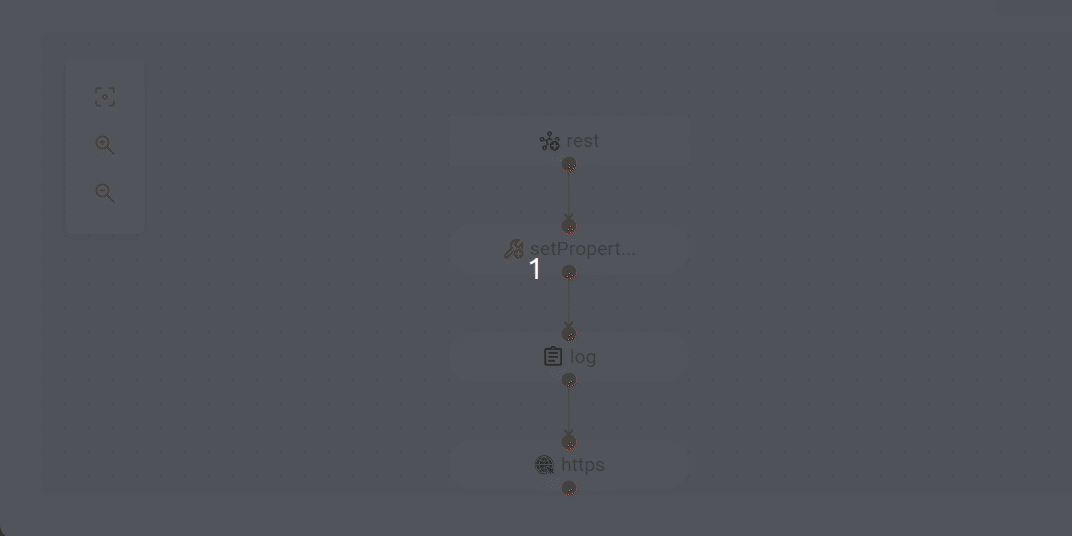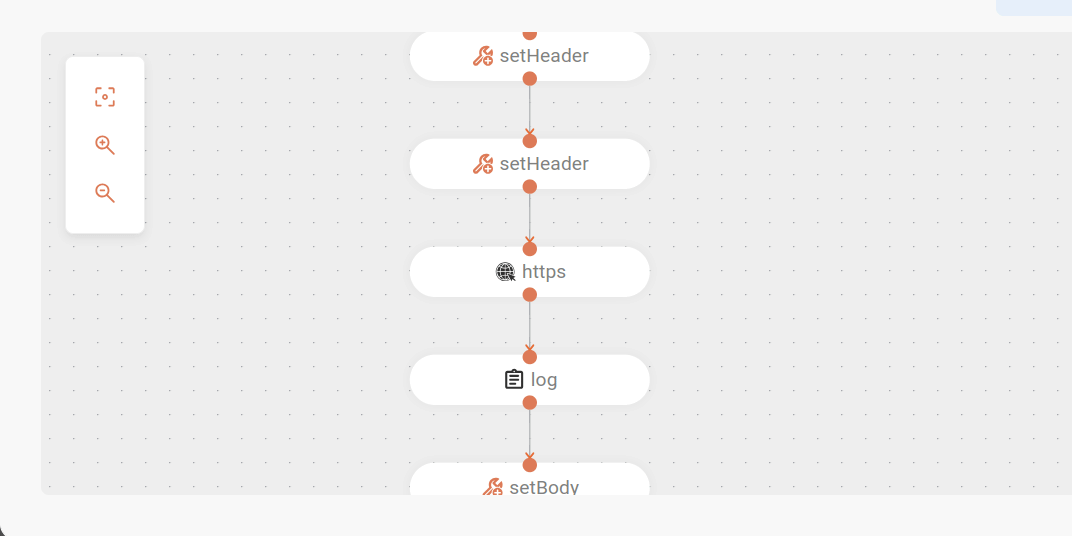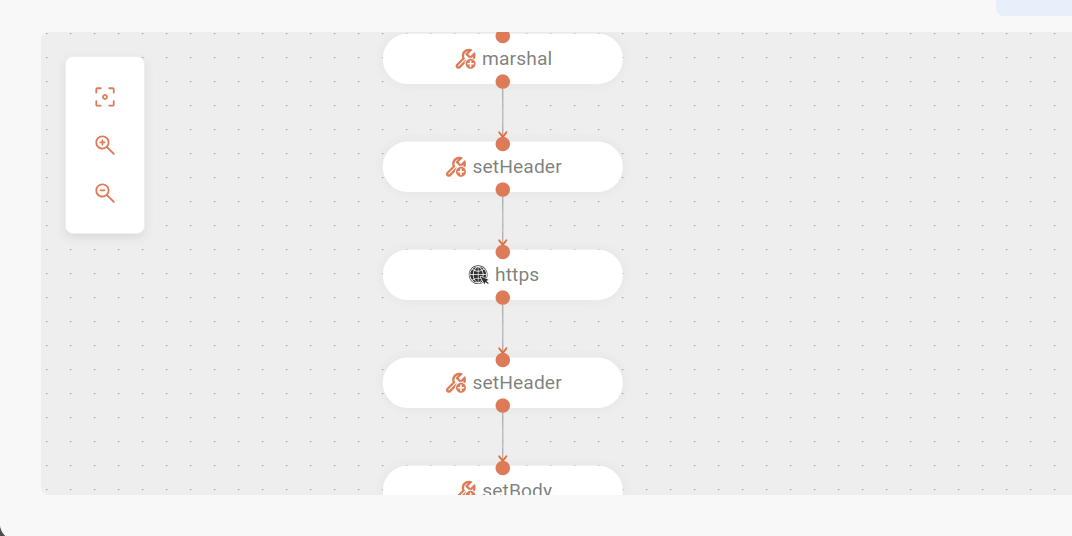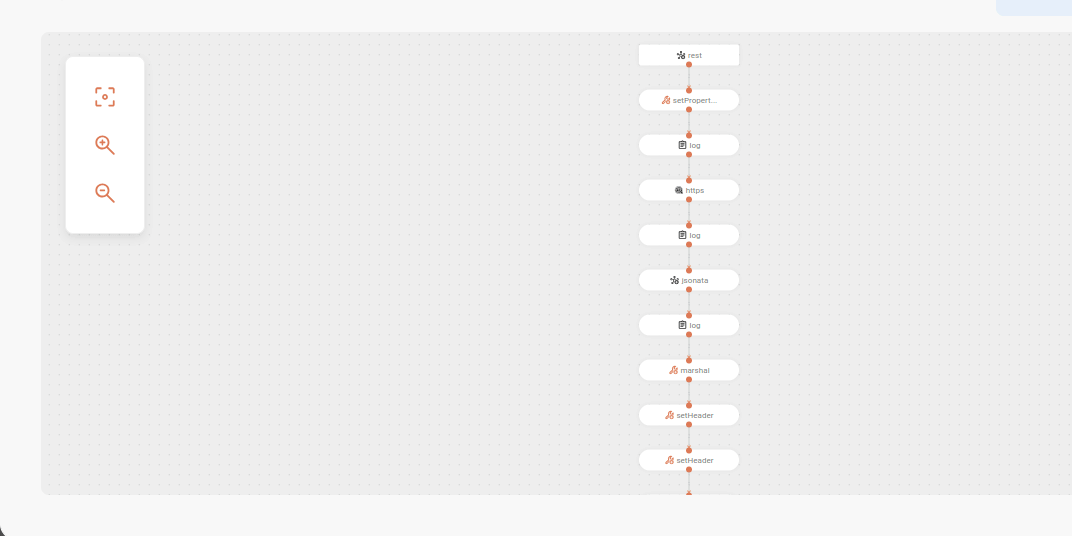
In the context of an e-commerce purchase, consider an integration that manages the payment processing through the following steps:
-
Order reception
-
Purchase information retrieval
-
Data transformation
-
Payment processing
-
Status update
-
Final response
Description of the steps
See below the description of the executed steps:
-
Order reception: the flow begins when an order is received with an identification code (ClientID). The
POSTrequest is forwarded to the/simpleendpoint. The response to the request is logged.- from: uri: rest:post:/simple - setProperty: expression: simple: expression: ${header[ClientID]} name: "clientID" - log: message: ${exchangeProperty.clientID} -
Purchase information retrieval: with the ClientID, the system queries an internal service for more details. The
GETrequest is made to the shopping endpoint, passing the ClientID as a parameter. The response to the request is logged.- toD: uri: https://{{URL}}/internal/purchases parameters: bridgeEndpoint: true httpMethod: GET ClientID: '${exchangeProperty.clientID}' - log: message: 'PURCHASES - ${body}' -
Data transformation: the received information is processed and formatted using a transformation tool, JSONata. The applied transformation is logged for verification.
- to: uri: jsonata:classpath:extractTotal.jsonata parameters: inputType: JsonString - log: message: 'TRANSFORMATION - ${body}'-
The instructions for creating a new JSON object are in the
extractTotal.jsonatafile, available in the Resources folder. -
The
extractTotal.jsonatafile is referenced in the flow script along with the classpath (snippet above). -
Below is the content of the
extractTotal.jsonatafile:{ "Account": Client.Account, "TypePayment": Client.TypePayment, "Value": $sum(Client.Orders.Product.(Price * Quantity)) }
-
-
Payment processing: the processed data is then sent to an external service to make the payment. First, the transformed message body is converted to JSON format, and the
Content-Typeheader (set to application/json) and theAuthorizationheader (with an example token) are configured. APOSTrequest is then made to the payment endpoint. The received response is logged.- marshal: json: library: Jackson - setHeader: expression: constant: expression: application/json name: Content-Type - setHeader: expression: constant: expression: 'Bearer AuthorizationTokenExample' name: Authorization - toD: uri: https://{{URL}}/external/payment parameters: bridgeEndpoint: true httpMethod: POST - log: message: 'PAYMENT - ${body}' -
Status update: after the payment is processed, the result is combined with the ClientID and transformed again to update the payment status in an internal service. The adjusted message body is converted to JSON format and sent in a
POSTrequest to the status endpoint.- setBody: expression: simple: expression: '{"ClientID": "${exchangeProperty.clientID}", "status":${body}}' - log: message: 'CONCATENATION - ${body}' - to: uri: jsonata:classpath:statusPayload.jsonata parameters: inputType: JsonString - log: message: 'STATUS PAYLOAD - ${body}' - marshal: json: library: Jackson - setHeader: expression: constant: expression: application/json name: Content-Type - toD: uri: https://{{URL}}/internal/status parameters: bridgeEndpoint: true httpMethod: POST-
The instructions for creating a new JSON object are in the
statusPayload.jsonatafile, available in the Resources folder. -
The
statusPayload.jsonatafile is referenced in the flow script along with the classpath (snippet above). -
Below is the content of the
statusPayload.jsonatafile:{ "ClientID": ClientID, "Status":status.status }
-
-
Final response: the system sends a final confirmation to indicate that the payment was successful. The HTTP response code is set to
200, and the response body confirms the success of the operation. Additionally, the content of the final response is logged.- setHeader: expression: constant: expression: "200" name: CamelHttpResponseCode - setBody: expression: simple: expression: '{"success": "true"}' - log: message: ${body}
Source Code
Below is the complete script for the integration flow:
- from:
uri: rest:post:/simple # Defines a REST endpoint that receives POST requests at the /simple route
steps:
- setProperty:
expression:
simple:
expression: ${header[ClientID]} # Stores the value of the 'ClientID' header in an exchange property called 'clientID'
name: "clientID"
- log:
message: ${exchangeProperty.clientID} # Logs the value of the 'clientID' property for debugging
- toD:
uri: https://{{URL}}/internal/purchases # Makes a GET request to the internal purchases endpoint
parameters:
bridgeEndpoint: true
httpMethod: GET
ClientID: '${exchangeProperty.clientID}' # Passes the 'clientID' as a parameter in the request
- log:
message: 'PURCHASES - ${body}' # Logs the response from the purchases request
- to:
uri: jsonata:classpath:extractTotal.jsonata # Processes the response using a JSONata transformation to extract the total
parameters:
inputType: JsonString
- log:
message: 'TRANSFORMATION - ${body}' # Logs the result of the JSONata transformation
- marshal:
json:
library: Jackson # Converts the message body to JSON using Jackson
- setHeader:
expression:
constant:
expression: application/json # Sets the 'Content-Type' header to 'application/json'
name: Content-Type
- setHeader:
expression:
constant:
expression: 'Bearer AuthorizationTokenExample' # Sets the 'Authorization' header with an example token
name: Authorization
- toD:
uri: https://{{URL}}/external/payment # Sends data to the external payment service via POST
parameters:
bridgeEndpoint: true
httpMethod: POST
- log:
message: 'PAYMENT - ${body}' # Logs the response from the payment service
- setBody:
expression:
simple:
expression: '{"ClientID": "${exchangeProperty.clientID}", "status":${body}}' # Builds a new JSON body with 'clientID' and the payment status
- log:
message: 'CONCATENATION - ${body}' # Logs the message body after concatenation
- to:
uri: jsonata:classpath:statusPayload.jsonata # Applies a JSONata transformation to format the status payload
parameters:
inputType: JsonString
- log:
message: 'STATUS PAYLOAD - ${body}' # Logs the generated status payload
- marshal:
json:
library: Jackson # Converts back to JSON
- setHeader:
expression:
constant:
expression: application/json # Sets the 'Content-Type' header to 'application/json' again
name: Content-Type
- toD:
uri: https://{{URL}}/internal/status # Sends the processed status to an internal service
parameters:
bridgeEndpoint: true
httpMethod: POST
- setHeader:
expression:
constant:
expression: "200" # Sets the HTTP response code to 200 (OK)
name: CamelHttpResponseCode
- setBody:
expression:
simple:
expression: '{"success": "true"}' # Sets the final API response indicating success
- log:
message: ${body} # Logs the final response| Advanced parameters for EIPs and components are not yet available in the configuration form of steps in the Diagram tab. To add them, use the Source Code tab. |
Share your suggestions with us!
Click here and then [+ Submit idea]