Data Transformation and Validation
CSV
-
Description: the CSV component is used to read and write data in CSV (Comma-Separated Values) format. It simplifies the handling of CSV files, enabling efficient data conversions and transformations.
CSV to JSON
-
Example
-
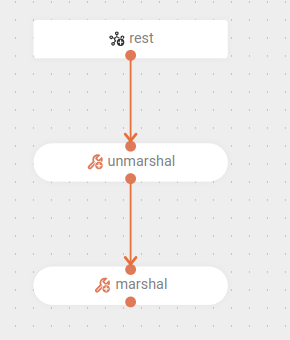
The route is triggered when a
POSTrequest is made to the/csv-to-jsonendpoint. -
The data in the request body, in CSV format, is deserialized (
unmarshal) into maps (useMaps: true) using the defined delimiter (delimiter: ","). -
These maps are transformed into JSON and returned as the response.
-
Script |
Diagram |
|
|
JSON to CSV
-
Example
-
The flow starts with a
POSTrequest to the/json-to-csvendpoint with data in JSON format. -
The received JSON is converted (
unmarshal) into an internal structure that can be manipulated (maps). -
The processed data is converted into CSV format (
marshal).-
Additionally, the delimiter
;(semicolon) is used to separate values and -
The headers
firstNameandlastNameare added.
-
-
Script |
Diagram |
|

|
| See more information about Data Format as a Camel component. |
JOLT
-
Description: the JOLT allows for transforming and manipulating JSON data declaratively, using specifications defined in JOLT files.
-
Example
-
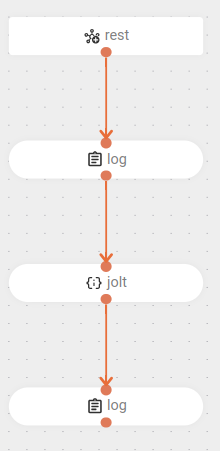
The flow starts with a
POSTrequest at the endpoint/jolt-poc. -
The request body is logged.
-
The flow transforms the request body using a Jolt template located in the
template.jsonfile.-
The parameters
inputType: JsonStringandoutputType: JsonStringensure that the input and output are handled as JSON strings. -
contentCache: trueenables caching of the results.
-
-
Finally, the flow logs the result of the transformation.
-
Script |
Diagram |
|
|
JSLT
-
Description: the JSLT component is used to transform data using templates written in JSLT. It processes input information, such as JSON or XML, reorganizing and formatting it according to a model that you define.
-
Example
-
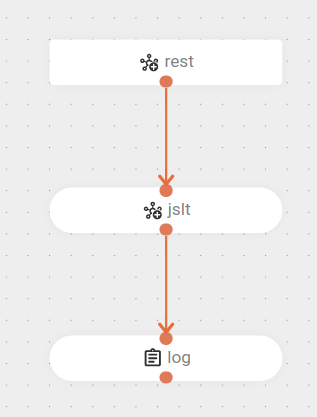
The flow starts with a
POSTrequest at the endpoint/hello. -
The request data is transformed using the JSLT component with the template file
expression.jslt.-
The parameter
contentCache=trueenables caching of the template content.
-
-
Finally, the transformed message is logged at the
infolevel.
-
Script |
Diagram |
|
|
JSONata
-
Description: the JSONata component allows processing and transforming JSON data using the JSONata query language. It enables complex operations such as filtering, transforming, and aggregating data.
-
Example
-
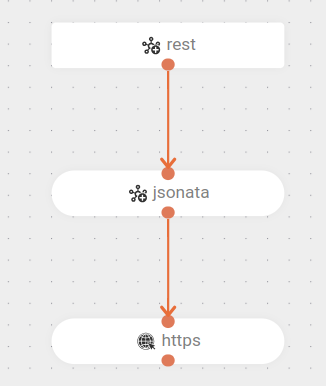
The flow starts with a
POSTrequest at the endpoint/jsonata. -
Then, the content of the request is transformed using a JSONata expression stored in the file
expression.jsonata. -
The parameters indicate that:
-
the results of the transformation can be cached (
contentCache: true); -
the input type for the transformation is a JSON string (
inputType: JsonString); -
the output type will also be a JSON string (
outputType: JsonString).
-
-
After that, the data is sent to an external endpoint via a
POSTrequest.
-
Script |
Diagram |
|
|
JSON Schema Validator
-
Description: the JSON Schema Validator component performs validation of the message body.
-
Example
-
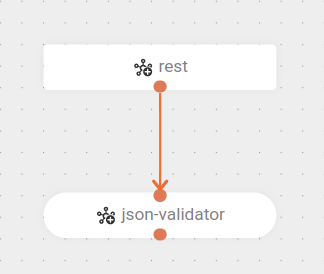
The flow starts when a
POSTrequest is received at the endpoint/hello. -
Then, the JSON validation component is used to check if the request body conforms to the schema defined in the file
my-json-schema.json.
-
Script |
Diagram |
|
|
XJ
-
Description: the XJ component allows converting XML and JSON documents without the need for intermediate Java objects.
-
Example:
-
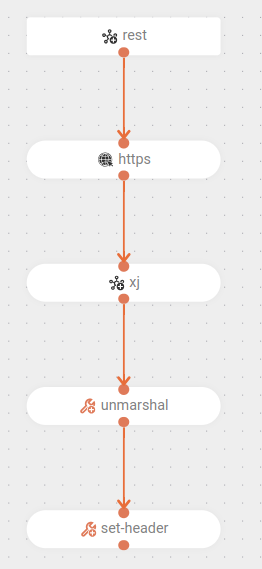
The flow starts by receiving a
POSTrequest at the/example-xjendpoint. -
It makes a
GETcall via HTTPS. -
It transforms the received XML response into JSON using the XSLT component.
-
The parameter
transformDirection: XML2JSONindicates the direction of the transformation, which in this case is from XML to JSON.
-
-
It converts the JSON into a Java object.
-
Finally, it sets the
Content-Typeheader toapplication/jsonto indicate the response type.
-
Script |
Diagram |
|
|
XSLT
-
Description: the XSLT component is used to transform XML documents using an XSLT stylesheet, allowing data to be converted into different formats or structures.
-
Example
-
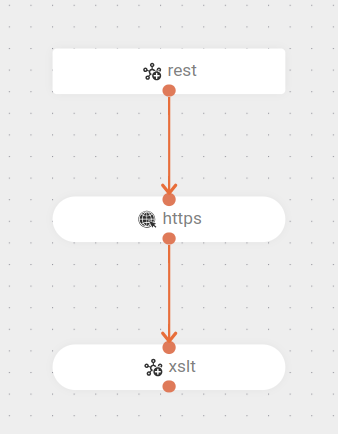
The flow starts with a
POSTrequest at the endpoint/source-xslt. -
The EIP
toDindicates that the flow should direct execution to a dynamic URI. -
The route then makes a
GETrequest, obtaining an XML response. -
It then transforms the XML response into JSON using an XSLT file:
response_to_json.xslt.
-
Script |
Diagram |
|
|
Share your suggestions with us!
Click here and then [+ Submit idea]